RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIALS (RCT)
RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIALS (RCT)
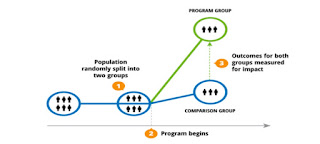
Randomized control trials are one of the most reliable methods for testing new drugs or therapy. It has become a standard for testing the level of safety and efficacy of an experimental drug that has to be proved by the pharmaceutical companies.
NEED FOR RANDOMIZATION
Randomization helps to avoid the incidence of BIAS. Both subjects and Investigators can influence when the researchers assign subjects to groups at random.
If the scientists are looking to demonstrate the ineffectiveness or potential danger of a certain treatment, they may assign participants who have a higher risk of complication or a lower chance of success to the group receiving the treatment. Researchers must disclose the potential conflict of interest when conducting a clinical trial
ADVANTAGES
1.Comparative
One treatment is directly compared to another
2.Minimises BIAS
Minimises allocation BIAS and selection BIAS
3. Confounding Factor minimization
Randomisation helps to minimize the unequal distribution of other associated factors in the study groups.
Randomisation makes the groups comparable according to both known factors and other unknown associated factors that may cause distortion.
Blocked randomisation makes groups comparable within known confounding
4.Publishable
Considered the gold standard, more publishable.
DISADVANTAGES
1.Logistics
Validity requires multiple sites which will be difficult to manage.
2.Statistics
Disadvantage of block randomization is the allocation of participants may be
predictable and results in selection BIAS when the study groups are unmasked.
3.Applicability
Trials which test for efficacy may not widely applicable. Trials which test for effectiveness are larger
and more expensive.
4.Ethical limitation
ICF is often Impossible
Some research cannot be ethically performed as an RCT.
TAKE AWAY
RCT is gold standard for testing the drug.
The participants are assigned to control and experimental groups randomly by the researcher. Selection BIAS may affect the results in such a way that the researcher or the funding agency is benefited with the scientific outcome of that particular study.
REFERENCE
1. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/280574
2. https://derangedphysiology.com
Qa q
By:-
Venkatesh.N
ClinoSol Student ID: 020/0222

Comments
Keep going..