PRECISION MEDICINE
PRECISION MEDICINE
DEFINITION:
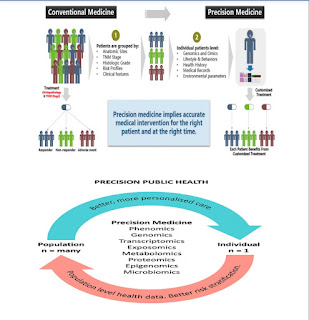
• Precision medicine is "an upcoming approach for disease treatment and prevention that consider individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person.
• This advance will allow doctors and researchers to forecast more precisely which treatment and prevention strategy for a particular disease will work in which groups of people.
• It is opposite to the one-size-fits-all approach, in which disease treatment and prevention strategy are developed for the standard person, with less consideration for the differences between individuals.
• In melanoma, precision medicine uses precise information about a person’s tumor to help make an analysis, plan treatment, find out how well treatment is effective, or make a diagnosis.
• Examples of precision medicine include using targeted therapies to treat exact types of cancer cells,like HER2-positive breast cancer cells, or using tumor marker testing to help to determine cancer. In addition called as personalized medicine.
• Even if the term "precision medicine" is quite new, the idea has been a part of healthcare for many years.
• For example, an individual who needs a blood transfusion is not given blood from a randomly selected donor; as an alternative, the donor’s blood type is matched to the recipient to lessen the risk of complications.
• Even though examples can be found in several areas of medicine, the responsibility of precision medicine in day-to-day healthcare is comparatively limited.
• Researchers wish that this approach will develop to many areas of health and healthcare in upcoming years.
PROBABLE BENEFITS OF PRECISION MEDICINE:
• Precision medicine helps health care providers helps be aware of the many things—including environment, lifestyle, and heredity—that play a part in a patient's health, disease, or condition.
• This information lets them more exactly predict which treatments will be most successful and safe, or probably how to prevent the illness.
• Transfer the stress in medicine from reaction to prevention
• Forecast vulnerability to disease
• Progress disease discovery
• Forestall disease advance
• Tailoring disease-prevention strategies
• Stipulating more effective drugs
• Evade prescribing drugs with expected negative side effects
• Lessen the time, cost, and failure rate of pharmaceutical clinical trials
• Get rid of trial-and-error inefficiencies that drive up health care costs and damage patient care
• Wider capability of doctors to use patients' genetic and other molecular information as part of routine medical care.
• Enhanced capability to foresee which treatments will work top for precise patients.
• Better understanding of the fundamental mechanisms by which different diseases occur.
• Enhanced approaches to preventing, diagnosing, and treating a wide series of diseases.
• Better incorporation of electronic health records (EHRs) in patient care, which will permit doctors and researchers to access medical data more easily.
CHALLENGES FACING PRECISION MEDICINE:
• Researchers will have to to discover ways to standardize the collection of clinical and hospital data from more than 1 million volunteers around the Nation.
• They will also need to propose databases to store large amounts of patient data proficiently.
• Cost is also an issue with precision medicine
• Doctors and other healthcare providers will need to know additional about molecular genetics and biochemistry.
• Now-a-days oncologists are no more treating cancer with a one-size-fits-all approach. They’re using precision medicine: a strategy in which the patients’ genes give the clues to potentially defeating their cancer.
PRECISION MEDICINE APPROACH IN TREATING CANCER:
• With precision medicine, we are currently in the place to make treatment decisions not just based on the specific cancer but on the genes that make up that cancer.
• By examining the DNA of a patient’s tumor, we can recognize the cancer-causing genes that make cancers nurture.
• With this information we have the talent to find a drug that targets that gene, so we can turn the gene off and attack the cancer cell.
• A fine example of the advancement made in outsmarting cancer with precision medicine can be seen in melanoma.
• We already know that there is one specific gene that is turned on by the sun and sunburn. It’s called B-RAF.
• This gene is mutated in over 60 percent of patients with melanoma.
• we don’t have any treatment options before, but now we have at least two drugs — vemurafenib and dabrafenib — that block B-RAF and prevents the cancer from growing.
• “With the ability to now sequence DNA, we can tell the patient which genes turn cancer on and which genes turn cancer off.”
• Precision medicine allows us to better identify the treatment from which the patient will get the most benefit.
• The plan is to essentially take the “speculation” out of drug selection.
• With precision medicine, we can now begin to recognize who will or who will not act in response to immunotherapy.
• It allows us to see the top drug treatments early on and puts the patient more quickly on the path to possible cancer cure while minimizing side effects.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN PRECISION MEDICINE:
• Artificial intelligence is a providing paradigm shift toward precision medicine.
• Machine learning algorithms are used for genomic sequence and to investigate and illustrate inferences from the enormous amounts of patients data and healthcare institutions recorded in every second.
• AI techniques are used in precision cardiovascular medicine to comprehend genotypes and phenotypes in presented diseases, progress the quality of patient care, permit cost-effectiveness, and ease readmission and fatality rate.
REFERENCES:
[1]U.S. National Library of Medicine "What are some of the challenges facing precision medicine and the Precision Medicine Initiative"? 22 September 2020
[2] Health Matters stories of science, care & wellness, What Is Precision Medicine? 2021 NewYork-Presbyterian
[3] Gustavo Rosa Gameiro, Viktor Sinkunas, [...], and José Otavio Costa Auler-Júnior Precision Medicine: Changing the way we think about healthcare 2018 Nov 23
[4] Geoffrey S Ginsburg and Kathryn A Phillips Precision Medicine: From Science to Value 2018 Jun 6.
[5]Seyhan, A.A., Carini, C. Are innovation and new technologies in precision medicine paving a new era in patients centric care?. 05 April 2019
[6] Euan A. Ashley 16 August 2016
AUTHOR:
HEMA DURGASI (PHARM D)
CSRPL_INT_ONL_WKD_208/0621
CLINOSOL INTERN TRAINEE_ BUSINESS DEVELOPER



Comments