CELLULITIS
INTRODUCTION
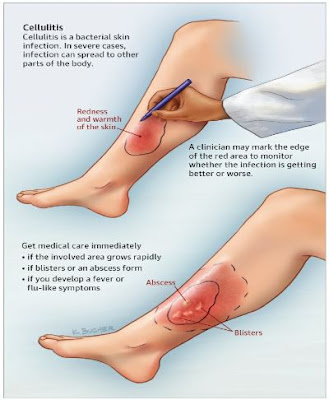
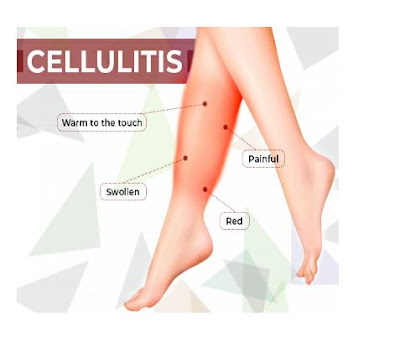
Cellulitis is a common serious bacterial skin infection. The skin appears swollen red and painful to touch and it affects deeper layers of skin. It is usually happening in the skin and sometimes may to deeper tissues and also blood streams and lymph nodes. It mainly affects lower legs and also on the face and other areas and it is not a contagious disease.
WHAT MAY CAUSE
 Cellulitis caused due to the bacteria mainly streptococcus or staphylococcus. These bacteria enter the skin when there is crack or any injuries over the body. Bug Bites like animal, insects, spider and tattoos are also some of the reason for infection.
Cellulitis caused due to the bacteria mainly streptococcus or staphylococcus. These bacteria enter the skin when there is crack or any injuries over the body. Bug Bites like animal, insects, spider and tattoos are also some of the reason for infection.SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
● Redness of the skin
● Fluid retention
● Pyrexia
● Pain at the site of infection
● Tenderness of skin
● Warmth
RISK FACTORS
● Weak body defences
● Injury
● Immunosuppressive drugs
● Skin diseases like eczema and diabetic foot
● Obesity
TYPES OF CELLULITIS
Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, including hands and legs. Depending on where the infection occurred, the cellulitis is classified,
They are
1. Facial cellulitis
2. Breast cellulitis
3. Perianal cellulitis
4. Periorbital cellulitis
Cellulitis is identified by medical history and physical examinations like redness, swelling, inflammation and fever.
The tests conducted for diagnosis of cellulitis are
1. White blood cell count
2. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
3. Culturing of fluid collected from abscess
4. Biopsy of injured area
TREATMENT
The treatment choice for cellulitis include taking antibiotics based on the suspected organism and presence or absence of pus, and pain relief drugs if there is excessive pain.
The antibiotics drugs can be taken as oral, intravenous, intramuscular. Steroids may also use for speed recovery. Patient usually responsive for oral antibiotic therapy if not responding to this therapy, doctor prescribes IV antibiotic treatment.
LIFE STYLE MODIFICATIONS
Following are the some of the modifications that help to recover from the cellulitis
● Drink plenty of water
● Elevate the infected area to reduce inflammation and pain
● Avoid scratching infected area
● Avoid alcohol and smoking
● Take balanced diet
Authors:
Ch. Niharika Chowdary
R. Ramkumar
MNR college of pharmacy
Sangareddy


Comments