CLINICAL TRIALS: PHASE AND CHALLENGES
CLINICAL TRIALS: PHASE AND CHALLENGES
Introduction:
Clinical research is a branch of sciences that determines the safety and effectiveness of medication, medical equipments and devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use. Clinical trials are the experiments and observations designed to answer specific questions about possible new treatments or new ways of using existing treatment regimens. The clinical trials play a crucial role in the detection, treatment, management and prevention of diseases and health related ailments which occur in human beings. The clinical trials have to be conducted with specific approved protocol and should fulfil all the necessary standard guidelines which are given by the ICH-GCP. The process of clinical trials is not a one time job, it has to be done in different phases with most care and caution as these trials directly affect the life of the participants.
Phases of clinical trials:
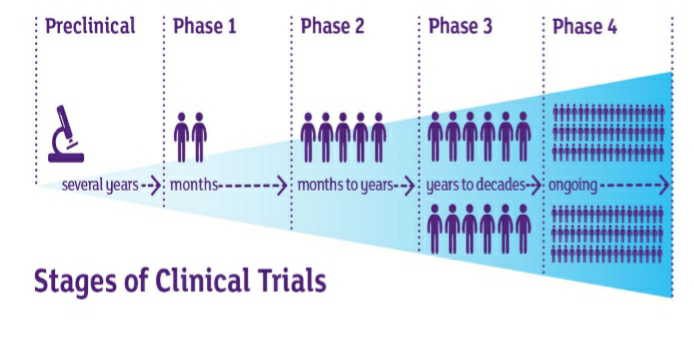
The process of clinical trial is done in different phases which are as follows:
- Phase-0:
In phase -0, the investigator uses a very small amount of doses to check whether the dose of medication is not harmful to the patients. This is done with little number of people, less than 15. The investigator has to do addition changes if the medication acts something expected or else can to further phases.
- Phase-1:
Phase 1 trials are also termed as Human Pharmacology studies. The phase 1 clinical trials are done for months for observing effects of medication on the subjects. This phase can be used to determine the highest dose for humans without any side effects. Phase 1 trials not only evaluate the ideal dose and safety but also the most suitable route of administration (i.e, oral, intravenous, tropical administration etc). Is it expected that about 70 % of clinical trials are approved for the next phases. Phase 2 trials are conducted on a population between 20 to 80 subjects. The subjects taken in this phase are healthy volunteers.
- Phase-2:
This phase is done for months to years with a subject population of hundreds. It is given to the people who are at the condition meant to treat with the new trial medication. In this phase the investigator observes for more side effects over more population than earlier phase. The success rate in phase II is about 33% and these move further into phase III.
- Phase 3:
Phase III trials are conducted to evaluate how the new trial medication works in comparison to the drug which is existing. The investigator has to demonstrate that the trial drug is more safe and efficient then the existing one. This can be done the randomisation process, which involves picking up the participants randomly and administering a group of people with medication and other group with the existing one. In this phase bias can be eliminated by conducting “Double-blind studies” in which neither the investigator nor the participant knows about the medication in the trial. As this phase involves large number of participants and long duration the chance of occurring side effects and serious adverse events is more likely. This phase involves a population above 2,000. If the investigator succeeds in demonstrating the safety and effectiveness and only the FDA approves the medication. It is estimated about 25-30% of medications trial in this phase is passed into phase 4.
- Phase 4:
This phase is also known as the post marketing surveillance trials. Phase IV clinical trials test the new drugs which are approved by the FDA after thorough completion of the prior phases. The drug is tested on several thousands of patients in order to derive a better knowledge on the short and long term side effects. The harmful effects discovered in this phase can consequently results in the restriction in the sale to certain groups of population or even ban on the drugs is imposed in more severe conditions.
Challenges in clinical trials:
In an industry or in any research, there will be number of challenges. The field of clinical research and trials are not exemption. The research team has to face many obstacles or challenges in order to complete the trial successfully, from the initial selection of the trial medication to the post marketing of the drug, challenges may occur at any point of course and in every phase of the trial there is a need to fulfil the guidelines and protocol of the research unconditionally. The completion of clinical trials takes years of times and huge investments, it is estimated that an amount of $300 millions been spent on a single trial. Before performing a clinical trial, investigators conduct preclinical researches using human cell culture or animal models.
- Complexity of Trials (21% of respondents)
Clinical trials have been increasing over the years. There are over 3.3 lakh of clinical trials which are registered till date and the design of the study is becoming more complex. The staffs working at the trial site is been at pressure in executing the trials designs. As the studies have to be designed in most simple and unobtrusive way for patients and that has to be accepted by the regulators and payers’.
Respondents at the trial sites are more concerned with meeting the challenge and focussing on the best study design in the world of complex modern clinical trials. This consciousness is because of high rate of failure to meet primary endpoints due to poor or complex design’.
- Regulations (15%)
Nowadays, the trials are been conducted at a global level and the regulations vary in some countries. There are countries where the industry are so heavily regulated, many respondents feel constrained by the complexity of the guidelines. Balancing the variations between different regulatory bodies will become a challenge to the researchers.
The number of trials is increasing gradually and they are looking forward to expand to the other countries trials and emerging markets in new countries. In this scenario, there will be a need to understand entire new sets of regulatory requirements and guidelines of the countries.
- Spiralling Costs (15%)
Due to the inevitable result in the complexity in study design and the varied regulations in different countries, the cost of trials is rising to all-time high. Increasing complexity of trials and tight timelines is putting more pressure on the requirement of resources to follow, implement and execute the clinical trial at every step.
- Patient access (12%)
The foremost important step in the initial stage of the trial is the process of Patient recruitment, which has to be done by unbiased randomized procedure and retention of the enrolled participants is also a major concern while running a trial. Most of the trials face a problem of not meeting the large number of trial participants and the increase in the drop outs rate is another drawback to the trial team. The decrease in the participants may not give accurate and prominent results. At times the sponsor has to give up his personal benefits in order to fully ensure the safety and financial benefits to the participants. Such instances enlighten the prevalence of patient centric approaches in today’s research.
- Staff Roles & Responsibilities (9%)
With the drastic increase in the complexity and rate of change in trials, the process of hiring and training of efficient and well qualified staff is also getting equally tricky. The selection and appointing of staff is becoming a challenge. There are certain roles and responsibilities assigned to the individuals in trial process. The evolution of these responsibilities to the CROs, CRAs, Investigators and other staff at the trial ensures the proper and systematic conduction of the trial. As discussed earlier, the field of clinical trials is expanding widely beyond countries and continents. So, recruiting the staff with a capability of working in varied work location is a big task. As the trials are becoming more and more geographically diverse, another new challenge is obtaining experienced clinical research professionals in developing and under developed countries.
- Technology (9%)
A technological advance plays a crucial role in improving many aspects of clinical trials and it seems as one of the great hopes for future trials. As there exists a number of new challenges in running, participating in and regulating trials. The selection to the most suitable and accurate technology is a challenge, as the selected technology has to gain acceptance from the patients and professions and approval from the regulators.
- Governance and oversight (9%)
For a successful completion of a trial there should be a strategic partnerships, vendors, study sites, CROs. Partnerships are playing a more important role in almost every aspect of trials today and the management and correlating each of the departments can often prove challenging.
From the perspective of a study site, one particular challenge is the ‘involvement of a huge number of vendors in the studies’.
- New drugs (5%)
Trials done for deriving more effective dose or routes for existing class of drugs is much different from trials done to discover new drugs. Brand new classes of drug require different ways of running trials. Cell therapies, genomics, personalised treatments. Discovering a drug will create a much bigger breakthrough in the treatment patterns bit the challenge is that the brand new drugs has to prove its safety and has to demonstrate the clinical effectiveness of the drug.
CONCLUSION:
Clinical trials are the sophisticated processes in the clinical research sectors and they are considered as the great boon to the wide population across the globe. The trial involves restless efforts of the clinical staff and research professionals. At every phase of clinical trial there will be a chance of errors and every stage is challenging to the research team. There is a need for potential framework and worthy strategies to overcome the challenges.
Overcoming of challenges will always be the key to success. Facing challenges will give breakthrough to the implementation of innovative ideas in the trials processes. Hence, challenges should never be a full stop for trials rather those must be stepping stones for the success and have to be utilized as a route way to the achievement of greater peaks in the clinical trials.
By:-
D.V.S NAGAPHANI SHARMA
Pharm. D


Comments